What Causes Hair Loss on Legs –Hair loss on the legs is a concern that affects both men and women. While many people focus on hair thinning or baldness on the scalp, hair loss on the legs can be an indicator of underlying health issues. Understanding the potential causes of hair loss on legs is crucial for identifying the appropriate treatment and maintaining overall well-being.
Common Causes of Hair Loss on Legs
1. Poor Circulation and Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
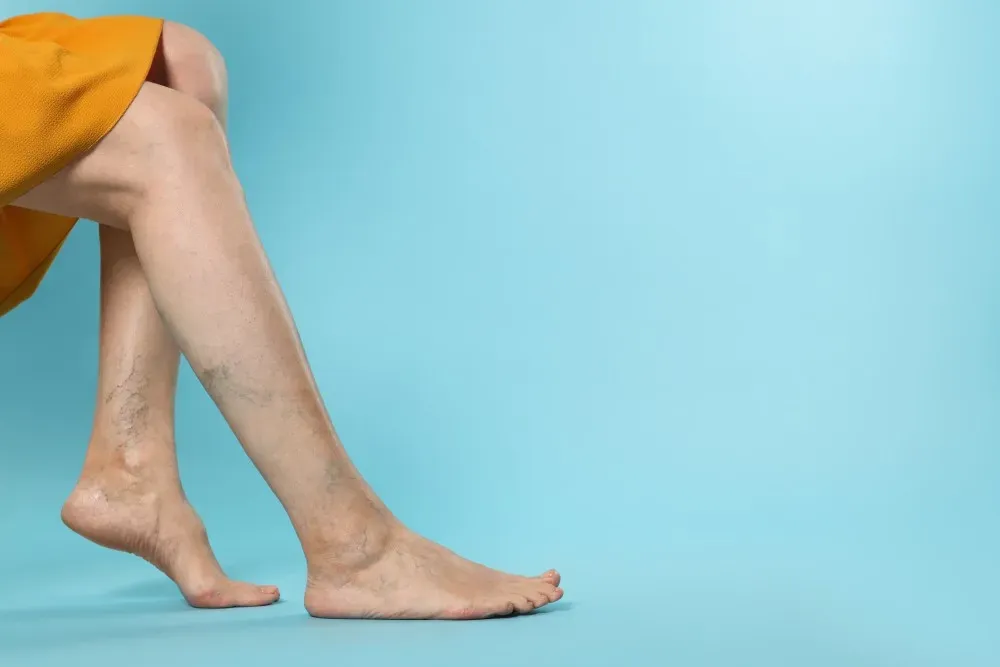
One of the most common causes of hair loss on legs is poor blood circulation. When blood flow to the legs is restricted, hair follicles do not receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients, leading to hair loss. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition where arteries narrow due to plaque buildup, reducing circulation to the lower extremities. This can cause:
- Hair loss on legs and feet
- Cold or numb feet
- Wounds that heal slowly
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a significant role in hair growth. Low testosterone levels in men or hormonal changes due to menopause in women can lead to reduced hair growth on the legs. Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can also contribute to hair loss by affecting the body’s ability to regulate hair growth cycles.
3. Skin Conditions and Infections
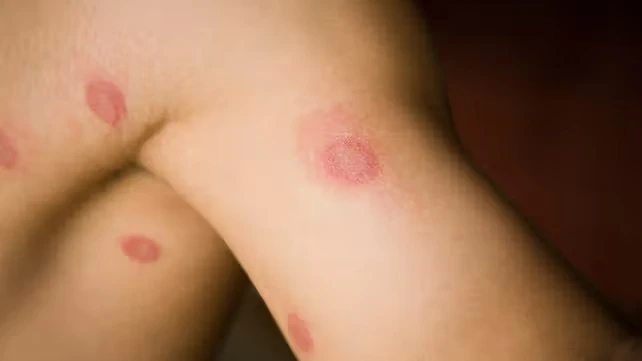
Certain skin conditions can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Common conditions include:
- Psoriasis – Causes excessive skin cell buildup, leading to inflamed patches that can affect hair follicles.
- Eczema (Dermatitis) – Leads to dry, scaly skin that may result in hair thinning.
- Fungal infections – Ringworm and other fungal infections can affect leg hair growth.
4. Friction and Trauma
Constant rubbing or friction from tight clothing, frequent leg crossing, or excessive scrubbing during showers can lead to hair loss on legs. This is commonly observed in athletes who wear compression gear or individuals who frequently wear tight pants.
5. Autoimmune Disorders

Autoimmune diseases like Alopecia Areata and Lichen Planopilaris cause the body’s immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on various parts of the body, including the legs. Lupus is another autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation and hair loss in different areas.
6. Medications and Treatments

Certain medications can have side effects that include hair loss on legs. These may include:
- Blood pressure medications
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Statins for cholesterol
If you notice hair loss after starting a new medication, consult your doctor about possible alternatives.
7. Nutritional Deficiencies

Hair growth requires essential nutrients such as:
- Iron – Low levels can lead to anemia and poor hair growth.
- Zinc – Essential for cell growth and repair.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7) – Important for healthy hair and nails.
- Vitamin D – Helps regulate the hair growth cycle.
A poor diet lacking in these nutrients can lead to hair loss, including on the legs.
8. Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders
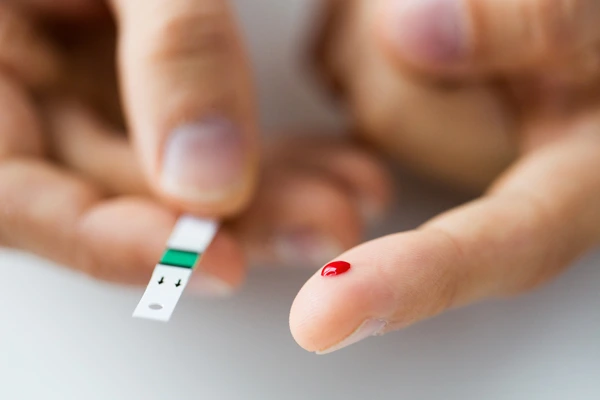
Individuals with diabetes often experience poor circulation and nerve damage, leading to decreased hair growth. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also cause inflammation and impact the body’s ability to grow and maintain hair on the legs.
9. Aging and Genetics

As people age, hair follicles become less active, and hair growth slows down. Genetics also play a role; if family members experience thinning leg hair, you may be genetically predisposed to the condition.
10. Shaving and Hair Removal Methods
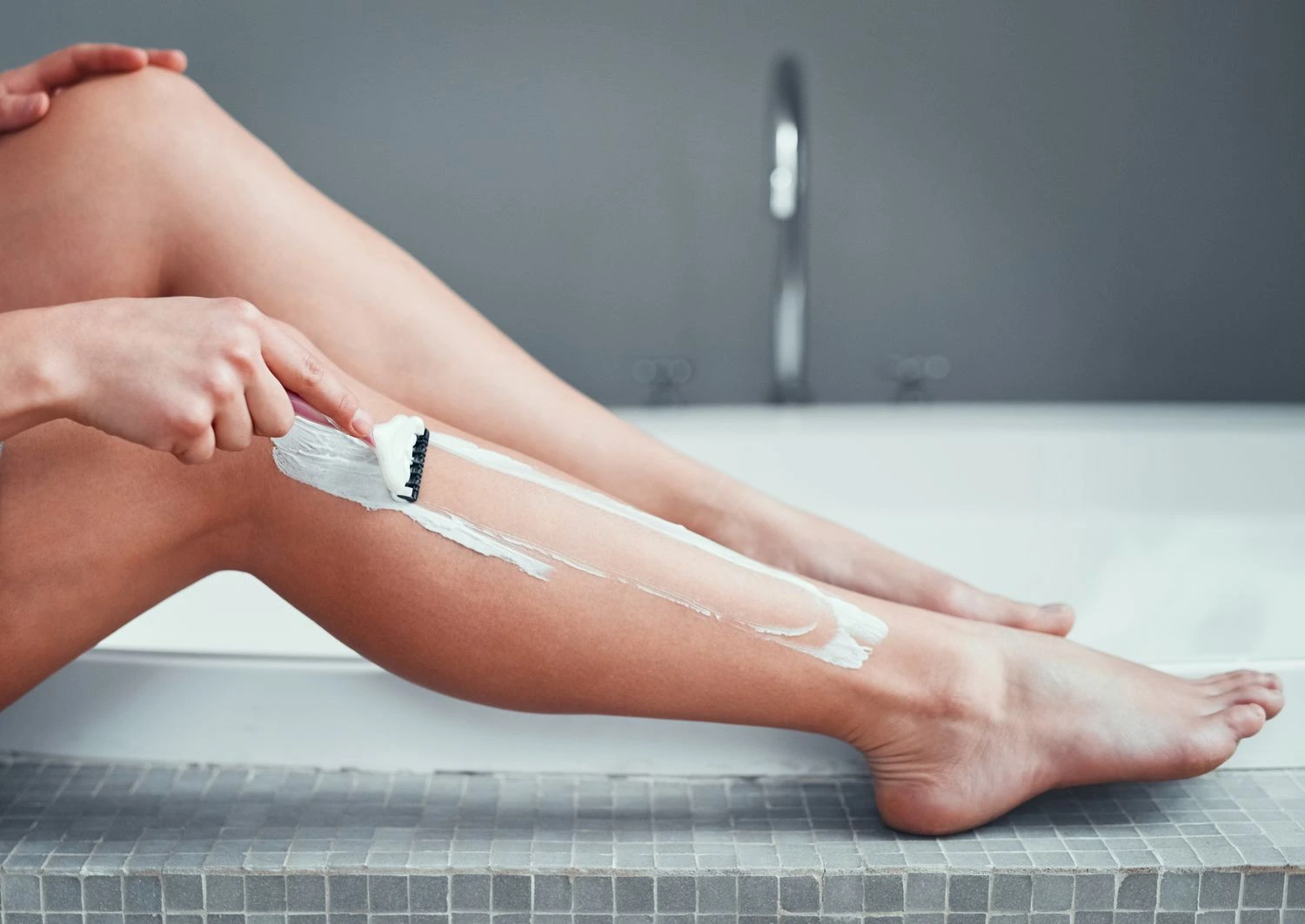

Frequent shaving, waxing, or using hair removal creams can sometimes lead to permanent hair loss due to repeated damage to the follicles. Over time, hair may grow back thinner or stop growing entirely.
How to Prevent and Treat Hair Loss on Legs

1. Improve Circulation
- Exercise regularly to boost blood flow to the legs.
- Avoid smoking, as it constricts blood vessels.
- Massage your legs to enhance circulation.
2. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Ensure you consume foods rich in iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamin D to support healthy hair growth.
3. Address Underlying Medical Conditions
If you suspect an underlying health issue such as PAD, thyroid disease, or diabetes, seek medical evaluation to receive the appropriate treatment.
4. Choose Gentle Hair Removal Methods
If hair removal is necessary, opt for less aggressive methods like electric shavers instead of waxing or chemical hair removers.
5. Avoid Tight Clothing
Wearing loose-fitting clothing can prevent friction-related hair loss and allow hair follicles to remain healthy.
6. Consider Medications or Topical Treatments
Certain topical treatments like minoxidil (Rogaine) may help stimulate hair growth on affected areas, though it is primarily used for scalp hair loss.
7. Consult a Dermatologist
If you experience sudden or severe hair loss on your legs, consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider to determine the cause and find appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
Hair loss on the legs can result from various factors, including poor circulation, hormonal imbalances, skin conditions, friction, autoimmune disorders, medications, and aging. Identifying the root cause is essential for finding the right solution. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, addressing medical conditions, and making necessary changes in hair removal habits, you can promote healthy leg hair growth and overall well-being.











